9 Strategies to Improve Average Position in Google Search Console
If you’re serious about SEO, you need to be well-acquainted with Google Search Console (GSC). That holds true whether you’re a small business on a budget or a large platform with money to spend — GSC delivers essential insights to help shape and track your SEO strategy, straight from the horse’s mouth.
While metrics like clicks, impressions, and CTR are fairly straightforward, there’s a fourth one that often gets misunderstood and overlooked: average position.
In this guide, I’ll break down what average position actually means, how it differs from other SEO metrics, and share nine practical strategies to help you improve your average position over time.
What Is Average Position in Google Search Console?
Average position in GSC refers to the average ranking of your website, individual pages, or a specific keyword across Google search results. When used effectively, it offers valuable insight into the strength of your SEO strategy by allowing you to track how your rankings evolve over time.
How Is It Average Position Calculated?
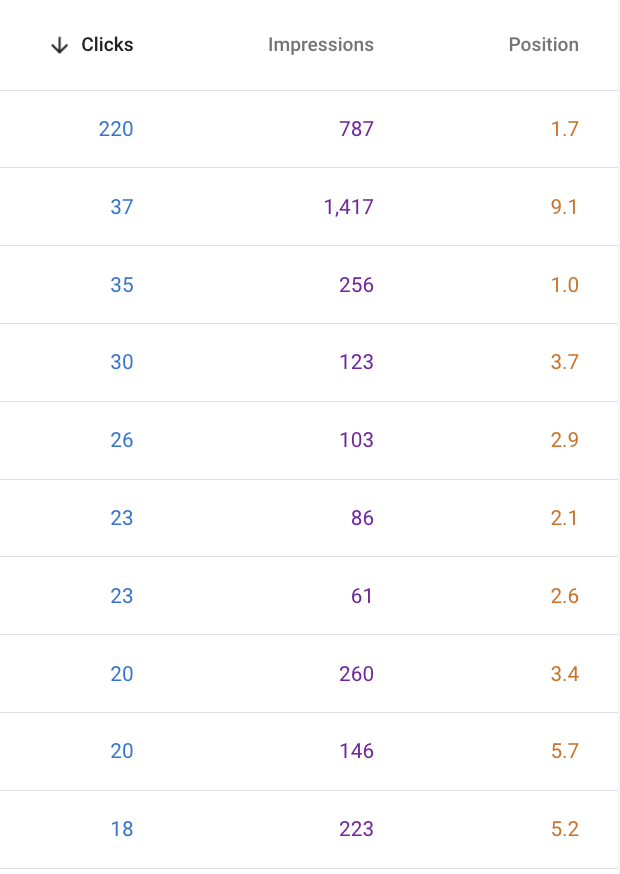
Every time one of your pages receives an impression — meaning the URL appears on a user’s screen — Google records the position where it showed up. Your average position is calculated by taking the mean of all these recorded rankings over a set time period.
Example: Your page receives four impressions, showing up in positions 1, 8, 5, and 12.
Average Position = (1 + 8 + 5 + 12) / 4 = 6.5
Worth noting: if your site appears multiple times for a query, Google only counts the highest-ranking result in the average.
Average Position vs. Search Ranking vs. PageRank
Let’s clear up a few common misconceptions:
Average Position is the mean ranking of a URL across all impressions.
Search Ranking typically refers to your current rank for a specific keyword — usually measured in a one-off snapshot.
PageRank is a legacy Google algorithm that ranked pages based on link authority (i.e., the quantity and quality of backlinks). It’s no longer publicly available or actively used for SEO reporting.
While search ranking gives you a moment-in-time view, average position offers a more comprehensive understanding of how your content performs across multiple searches, devices, and locations.
Why Average Position Matters
A higher average position generally means better visibility — which often leads to more clicks. While many factors can influence your average position, monitoring it consistently can help you:
Identify underperforming pages and queries
Evaluate whether your content aligns with search intent
Prioritize updates for pages that are close to reaching page one
Measure overall gains or losses in organic visibility
That said, don’t rely on it in isolation. Average position works best when considered alongside clicks, impressions, and click-through rate (CTR) to provide a fuller picture of your performance.
9 Strategies to Improve Average Position in Google Search Console
1. Refine On-Page SEO for Underperforming Keywords
Begin by identifying which pages or keywords have a high number of impressions but a low average position. These are excellent optimization opportunities and can often be improved with a few simple tweaks:
Include the focus keyword in your H1, title tag, meta description, and first hundred words of your page
Use keyword variations naturally within your content
Rework headers (H2s, H3s) to reflect relevant search terms
Improve readability with shorter paragraphs, bullet points, and formatting that aligns with SEO best practices
2. Optimize for Search Intent
Search intent is one of Google’s top ranking factors — so give the people what they’re looking for. If your content doesn’t match the user’s expectations, it’s unlikely to rank well.
Analyze the top-performing pages for your target keyword and ask:
Are they blog posts, product pages, or videos?
Do they offer quick answers or deep dives?
What brands or sources are ranking?
Then, align your content accordingly. For example, if you’re targeting an informational keyword with a sales page, consider creating a complementary blog post instead.
3. Update and Expand Existing Content
Your content doesn’t need to be brand new to perform well — but it does need to stay relevant. If a once-performing page starts to slip in rankings, it’s time for a refresh:
Update outdated facts, links, CTAs, and graphics
Add new subtopics, FAQs, or multimedia to enrich the page
Compare the page to top-ranking competitors — what are they covering that you’re not? What opportunities are they missing?
Adding unique insights or case studies to increase authority and value
4. Increase Page Time
Getting someone to click on your page is only half the battle — encouraging them to stay on the page is a big part of maintaining your ranking. Make your page more enjoyable by:
Putting your most valuable info up top. Don’t bury the lead — users often bounce before they reach the bottom of the page.
Embedding supporting media. Videos, infographics, image galleries, and even social embeds can help maintain attention.
Being mindful with popups. Avoid oversized or hard-to-close popups, and limit them to once per session if possible. The more annoying they are, the more likely they’ll drive users away.
5. Use Internal Linking Strategically
Google crawls your site by following internal links, and pages with more quality internal links often rank higher. Use a hub-and-spoke model where relevant blog posts or service pages link back to your core content. Make sure:
Anchor text reflects the page’s keyword focus
Links are placed early in the content for better visibility
You link to underperforming pages from your most authoritative ones
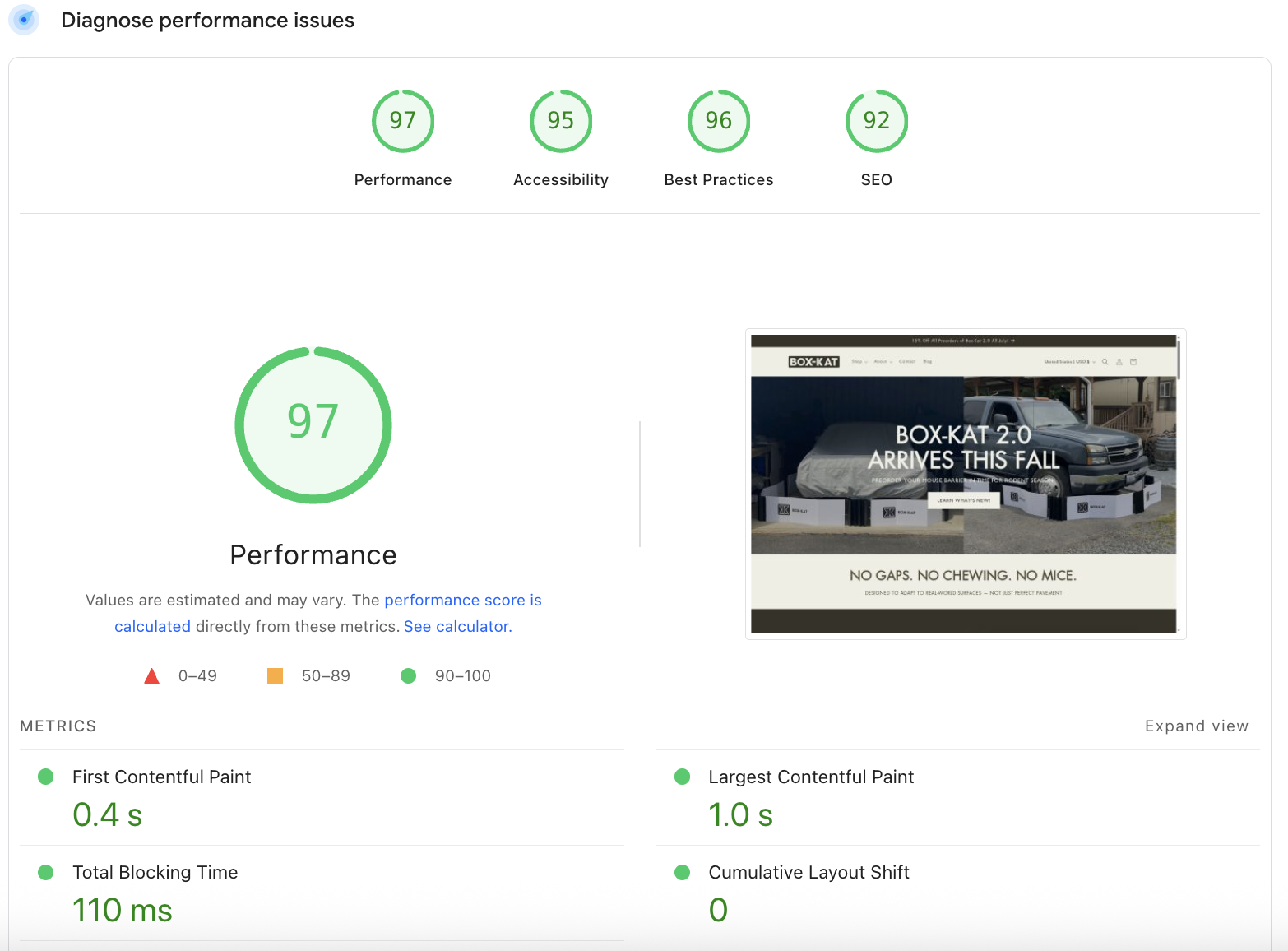
6. Improve Core Web Vitals and Page Speed
PageSpeed Insights for Box-Kat.com
Even the best content strategy will go to waste if your site’s technical performance is failing. Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights or Core Web Vitals report to identify issues with:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Optimize so key elements load quickly
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Prevent visual shifting as the page loads
Speed Index: Reduce load times by streamlining scripts and compressing images
These factors directly influence user engagement, bounce rates, and ultimately, your average position.
7. Earn High-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks from credible websites remain one of the strongest signals of authority. The more high-quality sites link to your content, the more likely Google is to reward it with better positioning.
Here are a few proven ways to build them:
Create linkable assets: guides, templates, stats, or tools others want to reference
Pitch content or guest post ideas to journalists, bloggers, or niche publishers
Use platforms like HARO (Help a Reporter Out) to offer quotes and gain exposure
Run a link gap analysis to identify where competitors are getting backlinks that you’re not
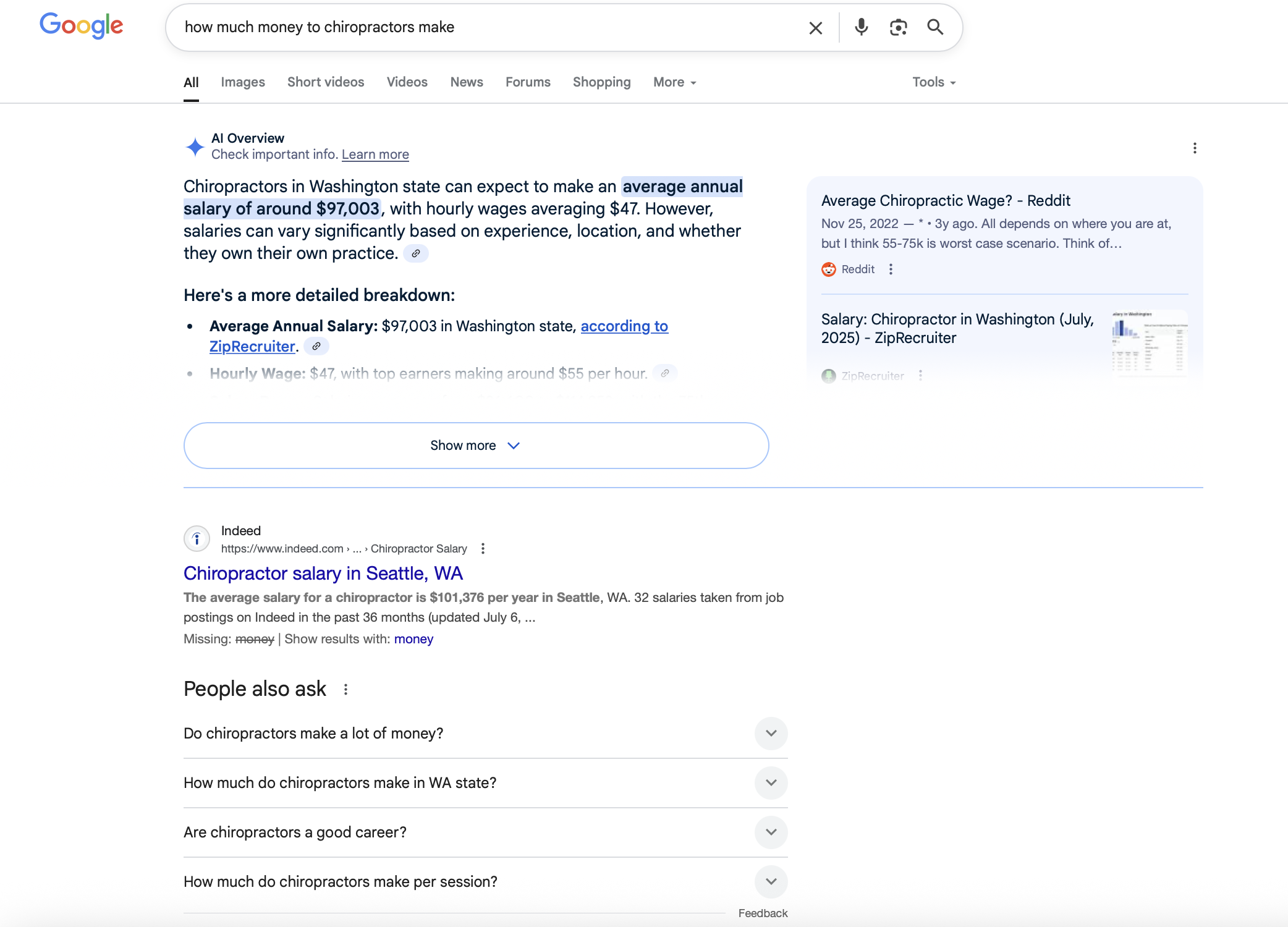
8. Target Featured Snippets, SERP Enhancements, & AI Overviews
SERP with AI Overview and People Also Ask enhancement
These result types appear above the traditional first result, offering a shortcut to significantly higher visibility. To improve your chances of earning one:
Use clear, structured headings that align with common search queries
Write short, direct answers to commonly asked questions near the top of the page
Format content using bullet points, numbered lists, and tables
Implement schema markup (FAQ, How-To, Review, etc.) to qualify for enhanced results like featured snippets or AI-generated summaries
9. Consolidate Competing Content
If you have multiple pages targeting similar keywords, they might be cannibalizing each other — splitting traffic and confusing search engines. Fix this by:
Auditing overlapping content using tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or Screaming Frog
Deciding which page should “win” based on performance indicators like backlinks or conversions
Merging weaker pages into a single, stronger one and redirecting the old URLs
Ensuring the new consolidated page is comprehensive, well-organized, and clearly focused on the topic
How to Track Progress in Google Search Console
To measure the impact of your optimization efforts, Google Search Console’s Performance report is your go-to dashboard. Here's how to track improvements effectively:
Set a consistent date range — Compare data over a 28-day or 3-month period to avoid skewed snapshots.
Filter by individual queries or pages — Focus on the specific pages or keywords you've optimized.
Use the comparison feature — Compare two time periods (e.g., before and after updates) to track movement in average position.
Segment by device or location — Discover if changes are more effective on mobile versus desktop or in certain regions.
Monitor impressions, clicks, and CTR alongside average position — Position improvements that don’t lead to more clicks may indicate a misalignment with intent or poor meta copy.
When to Stop Obsessing Over Average Position
While average position is a helpful metric, it shouldn’t be your north star. Here’s when to step back:
Minor fluctuations are normal. A small shift from 6.4 to 6.7 may have no impact on traffic or conversions.
A lower average can signal broader visibility. If your site starts ranking for more keywords — including some with lower positions — your average may drop even while your traffic goes up. That’s not a bad thing.
Focus on impact-driven queries. Prioritize performance on high-converting or brand-building keywords rather than trying to boost every single position.
CTR and conversions matter more. Being No. 1 doesn’t mean much if no one clicks. Sometimes improving your meta title or rich results leads to better performance than climbing a spot or two.
Use average position as a trend indicator — not a scoreboard. It’s one of many data points that should guide, but not dominate, your SEO strategy.
Want Help Improving Your Average Position?
Improving your average position in Google Search Console comes down to a simple formula: align your content with what users are searching for, keep your site technically sound, and make ongoing improvements based on real performance data.
Simple — yes. But not always quick.
The strategies above will help you climb the SERPs, increase visibility, and attract more qualified traffic. But if you’d like a second pair of eyes (or just want to speed up the process), reach out today for a free SEO audit of your site. I’ll help you identify what’s working, what’s not, and where the biggest opportunities lie.
FAQ
What is a good average position in Google Search Console?
Generally, anything under 10 means you’re on the first page. Under 5 is ideal for high traffic.
How often is average position updated?
GSC updates its performance data every 24–48 hours.
Can you manually change average position?
Not directly. It improves as you enhance your SEO and gain authority.
Why does average position go down even if traffic increases?
You may be ranking for more keywords — including lower-positioned ones—which lowers the average but expands reach overall.